As a physician, it's crucial to shed light on osteoporotic spine fractures, a condition that can significantly impact the health and well-being of individuals, particularly as they age.
Introduction:
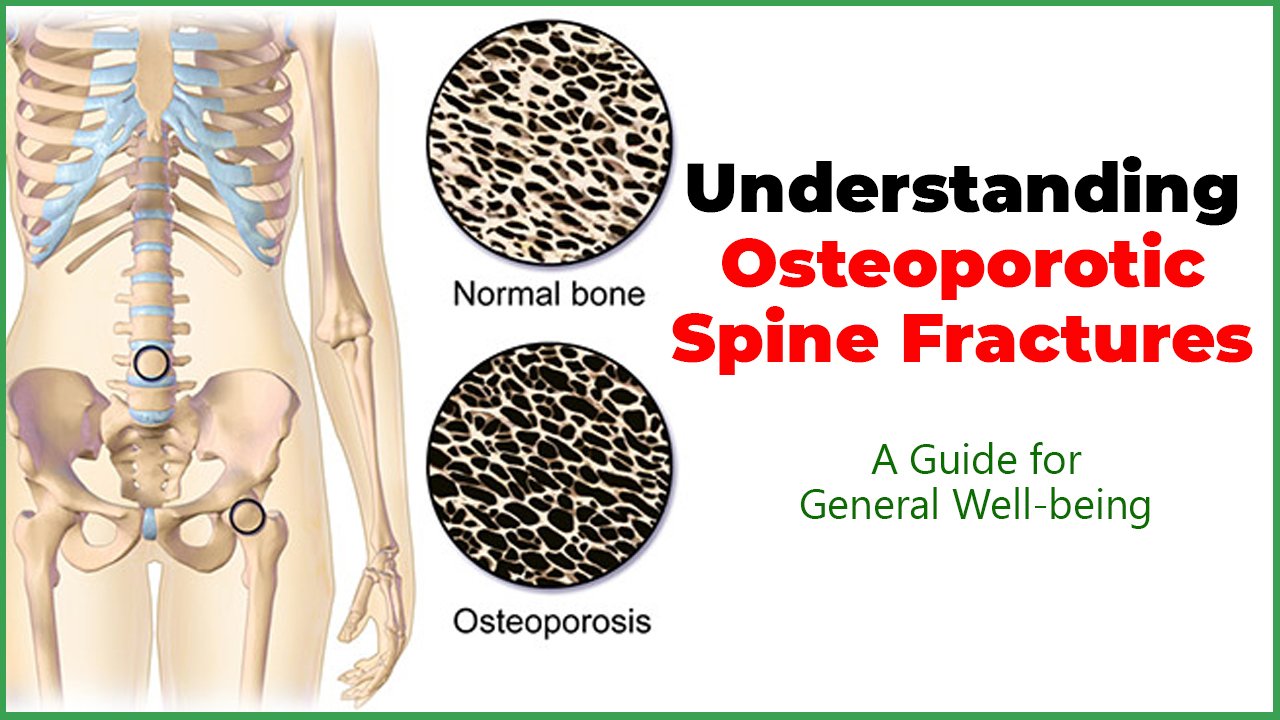
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. One of the common consequences of osteoporosis is spine fractures, which can have profound effects on an individual's mobility and quality of life.
What is Osteoporotic Spine Fracture?
Osteoporotic spine fractures occur when the vertebrae, the small bones that make up the spine, become weakened and porous due to the loss of bone density. These fractures often result from routine activities, such as bending or lifting, and can cause pain, deformity, and a decrease in height.
Risk Factors:
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoporotic spine fractures. Age, gender (women are more prone), genetics, and a lack of calcium and vitamin D in the diet can increase the risk. Additionally, certain medications and chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can exacerbate the likelihood of fractures.
Prevention:
Preventing osteoporotic spine fractures involves a multifaceted approach. Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, along with weight-bearing exercises, can help maintain bone density. Regular screenings and bone density tests, especially for postmenopausal women and older adults, can aid in early detection and intervention.
Symptoms:
Osteoporotic spine fractures may manifest as sudden or gradual onset of back pain, height loss, or changes in posture. It's essential to pay attention to these signs, as early identification can lead to more effective management.
Treatment:
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the fracture. Conservative measures may include pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. In some cases, surgical interventions might be necessary to stabilize the spine and alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Patients diagnosed with osteoporosis should adopt a bone-healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in regular exercise, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and following prescribed medications.
Conclusion:
Osteoporotic spine fractures are a serious consequence of bone fragility, especially in aging populations. As a physician, it's crucial to educate individuals on preventive measures and encourage a proactive approach to bone health. By fostering awareness and implementing lifestyle changes, we can collectively work towards reducing the impact of osteoporotic spine fractures and promoting overall well-being.